What do we know about CBD?

Introduction to CBD
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring compound found in the resinous flower of cannabis, a plant with a rich history as a medicine, dating back thousands of years. Today, the therapeutic properties of CBD are being tested and validated by scientists and doctors around the world. Safe, non-addictive, Cannabidiol is one of over one hundred “phytocannabinoids” that are unique to cannabis and give the plant its strong therapeutic profile.
Cannabidiol is closely related to another important drug-active phytocannabinoid: tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), a compound that induces the euphoric and elevated states for which cannabis is famous. These are the two components of cannabis that has been the most studied by scientists.
Both Cannabidiol and THC have significant therapeutic properties. But unlike THC, CBD doesn’t make a person feel “high” or intoxicated. This is because Cannabidiol and THC act differently on different receptors in the brain and body.
CBD can actually reduce or neutralize the psychoactive effects of THC, depending on how much of each compound is consumed. Many people want the health benefits of cannabis with no or less highs. The fact that CBD is therapeutically powerful as well as non-intoxicating and easily taken as oil makes it an attractive treatment option for those who are cautious. to try this component for the first time.
CBD: a multifunctional molecule
Many people are looking for alternatives to pharmaceuticals with harsh side effects – medicine is more in sync with natural processes. By leveraging the way we biologically function at a deep level, CBD can provide relief from chronic pain, anxiety, inflammation, depression, and many other conditions.
Extensive scientific research – much of which is sponsored by the US government – and an increasing number of anecdotal reports from patients and doctors highlight the potential of CBD as a treatment for a wide range of conditions, including (but not limited to):
- Autoimmune diseases (inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Neurological diseases (Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, Huntington’s chorea, stroke, traumatic brain injury)
- Metabolic syndrome (diabetes, obesity)
- Psycho-neurological diseases (autism, ADHD, PTSD, alcoholism)
- Bowel disorders (colitis, Crohn’s disease)
- Cardiovascular disorders (atherosclerosis, arrhythmia)
- Skin diseases (acne, dermatitis, psoriasis)
CBD has proven neuroprotective effects, and its anti-cancer properties are being studied at several academic research centers in the United States and other countries. A 2010 Brain Cancer Study by California scientists showed that CBD “enhances the inhibitory effect of THC on the proliferation and survival of human glioblastoma cells.”

Delta-8 Gummies – Gold Paradise Mix
Original price was: $82.99.$38.99Current price is: $38.99.
Or Subscribe and Save 30%

Silver Paradise Mix
Original price was: $68.99.$33.99Current price is: $33.99.
Or Subscribe and Save 30%
How does CBD work?
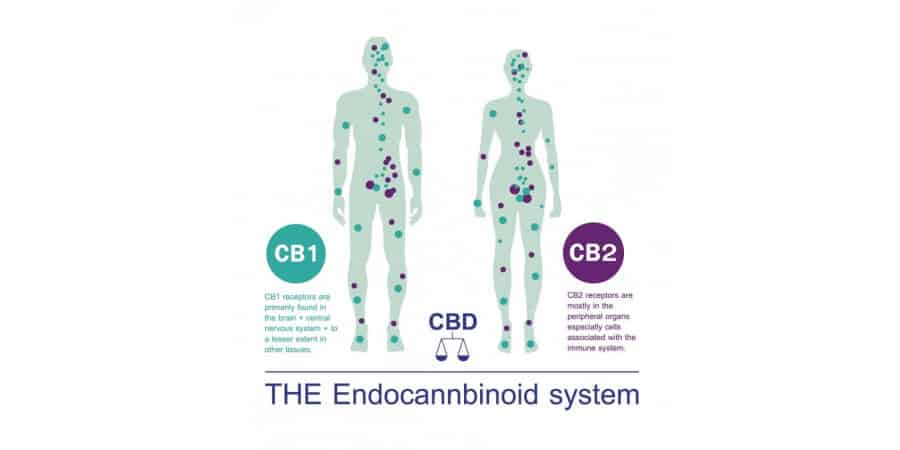
CBD and THC interact with our bodies in a variety of ways. One of the main ways is to mimic and enhance the effects of compounds in our body called “endogenous cannabinoids” – as they are called because of their similarity to compounds found in the cannabis plant. These “endocannabinoids” are part of what scientists call the “endocannabinoid system”.
The discovery of the endocannabinoid system has greatly advanced our understanding of health and disease. This has serious implications for almost every area of medical science and helps explain how and why CBD and THC are such versatile compounds – and why cannabis is such a widely consumed plant despite its illegal status.
The endocannabinoid system plays a critical role in regulating a wide range of physiological processes that affect our daily experience – our mood, our energy level, our intestinal resilience, immune activity, blood pressure, bone density, glucose metabolism, how we experience pain, stress , hunger and more.
What happens if the endocannabinoid system is not functioning properly? What are the consequences of a chronically deficient or overactive endocannabinoid system? In a word, a disease.
Modern science has shown that the endocannabinoid system is disrupted in almost all pathological conditions. Thus, it makes sense that “modulating the activity of the endocannabinoid system may have therapeutic potential for almost all diseases affecting humans,” as suggested in a publication of the year by Pal Pacher and George Kunos, scientists at the US National Institutes of Health (NIH).
By modulating the endocannabinoid system and increasing endocannabinoid tone, CBD and THC can slow – or in some cases stop – disease progression.